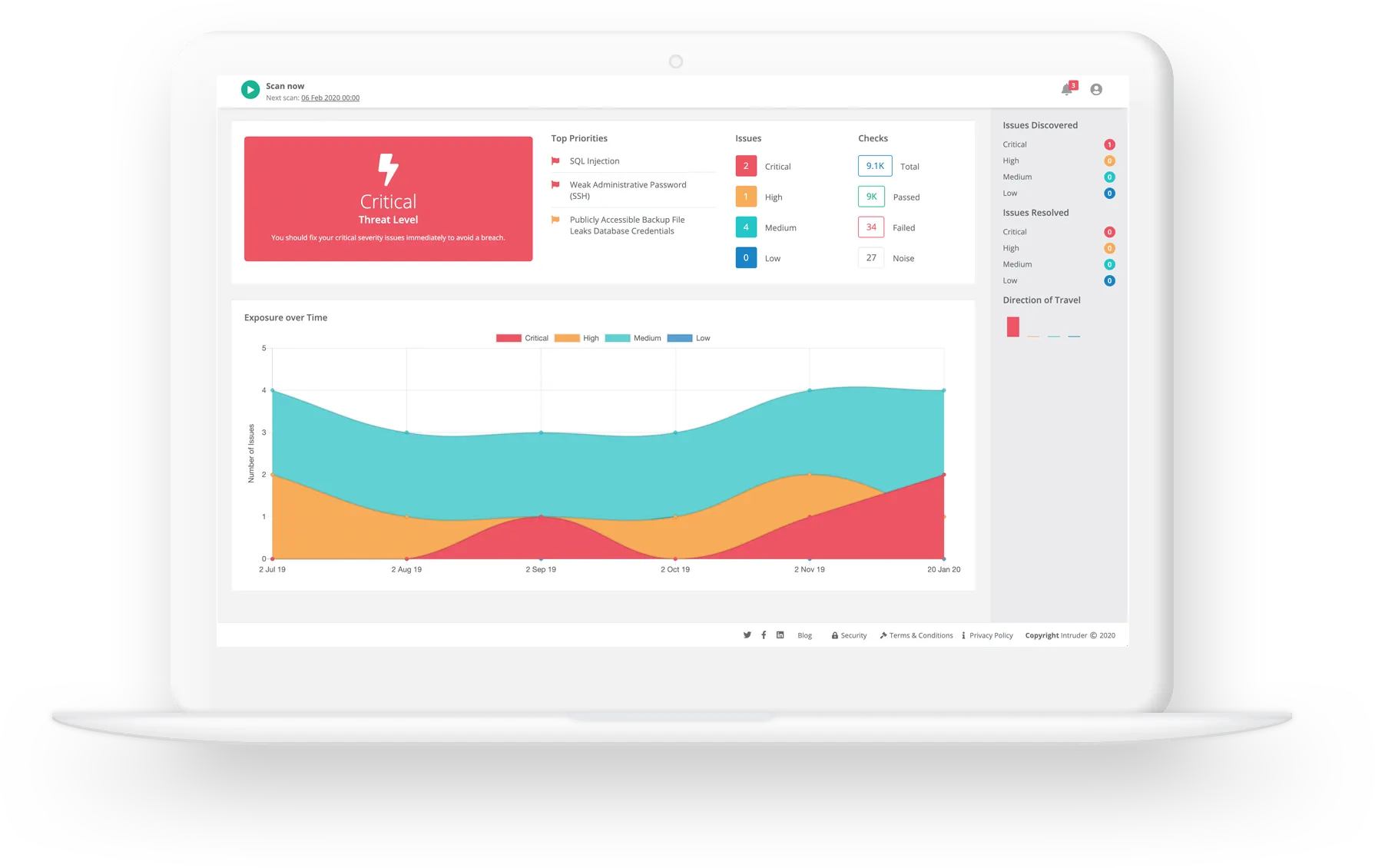
Key Points
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is a compliance standard designed to manage information security. It provides a robust framework for creating and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Created and managed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), it is underpinned by three core principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability of information.
It is internationally recognized and the go-to standard for information security (infosec), so obtaining ISO 27001 compliance sends a powerful message to your customers, clients, regulators, staff and other stakeholders that your organization is committed to upholding the highest security standards.
Who needs ISO 27001 certification?
According to ISO, over 70,000 ISO 27001 organizations are certified in over 150 countries – spanning all industries, but especially those in risk-averse sectors such as finance, healthcare, and defense.
Although it’s a natural fit for these types of organizations, ISO 27001 can be beneficial to anyone that needs to prove that the sensitive information they store is safe, regardless of company size. The standard demands that controls, procedures and risk management is airtight, which can boost customer confidence and, in turn, open up more business opportunities.
Why is ISO 27001 important?
Cyber threats are both amorphous and relentless, making cyber security a priority for all, but a daunting prospect for some. Fortunately, the holistic approach to information security provided by ISO 27001 makes it a good foundation for organizations keen to improve their security posture.
By integrating information security principles at the core of your organization and reducing the burden on maintenance and removing the mystery often associated with it, ISO 27001 compliance can help ingrain security in all your processes and controls, so it’s not something that has to be introduced as a standalone consideration.
What are ISO 27001’s controls?
ISO 27001 consists of 114 security controls grouped into 14 areas:
- Information security policies
- Organization of information security
- Human resources security
- Asset management
- Access control
- Cryptography
- Physical and environmental security
- Operations security
- Communications security
- Systems acquisition, development and maintenance
- Supplier relationships
- Information security incident management
- Information security aspects of business continuity management
- Compliance
These controls will help you understand the gaps present in your current operations and processes, and then close or mitigate the risks associated with these.
How can vulnerability management help with ISO 27001 compliance?
Vulnerability management is simply best practice for every modern business today, and continuous monitoring should be integrated into your ISO 27001 controls. Vulnerability management can help to identify risks before exploitation or compromises, as well as improve the overall security posture for ISO 27001 compliance and audits.
FAQs
Is vulnerability scanning required for ISO 27001 compliance?
Although not actually specified by ISO 27001, it is highly recommended to run regular vulnerability scans to maintain visibility of your attack surface and get ahead of potential risks introduced by new, emerging or recurring vulnerabilities.
Is penetration testing required for ISO 27001 compliance?
Similar to vulnerability scanning, penetration testing isn’t a specific requirement for ISO 27001, however, it is considered best practice to conduct regular pentests.
How Intruder can help you achieve ISO 27001 compliance
ISO certification doesn’t need to be difficult with Intruder. Get audit-ready reports, continuous monitoring, integrations with Drata, Vanta, and more. Intruder takes the pain out of ISO 27001 compliance by automating and streamlining the reporting process, reducing both the cost and time of compliance. Why not try it for free for 14 days or get in touch to find out more.















![Top Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools [2024]](https://assets-global.website-files.com/61dd9339d05701829d0b3241/63a1911637e85e9bd7752961_Web%20app%20security%20testing%20thumbnail.jpg)